Choking emergencies can happen suddenly and without warning, posing a serious threat to life. Recognizing the signs of choking and responding rapidly are crucial skills that can make the difference between a swift recovery and a life-threatening situation. In this article, we’ll explore the urgency of choking emergencies, shed light on common choking hazards for various age groups, and emphasize the importance of quick and effective responses.
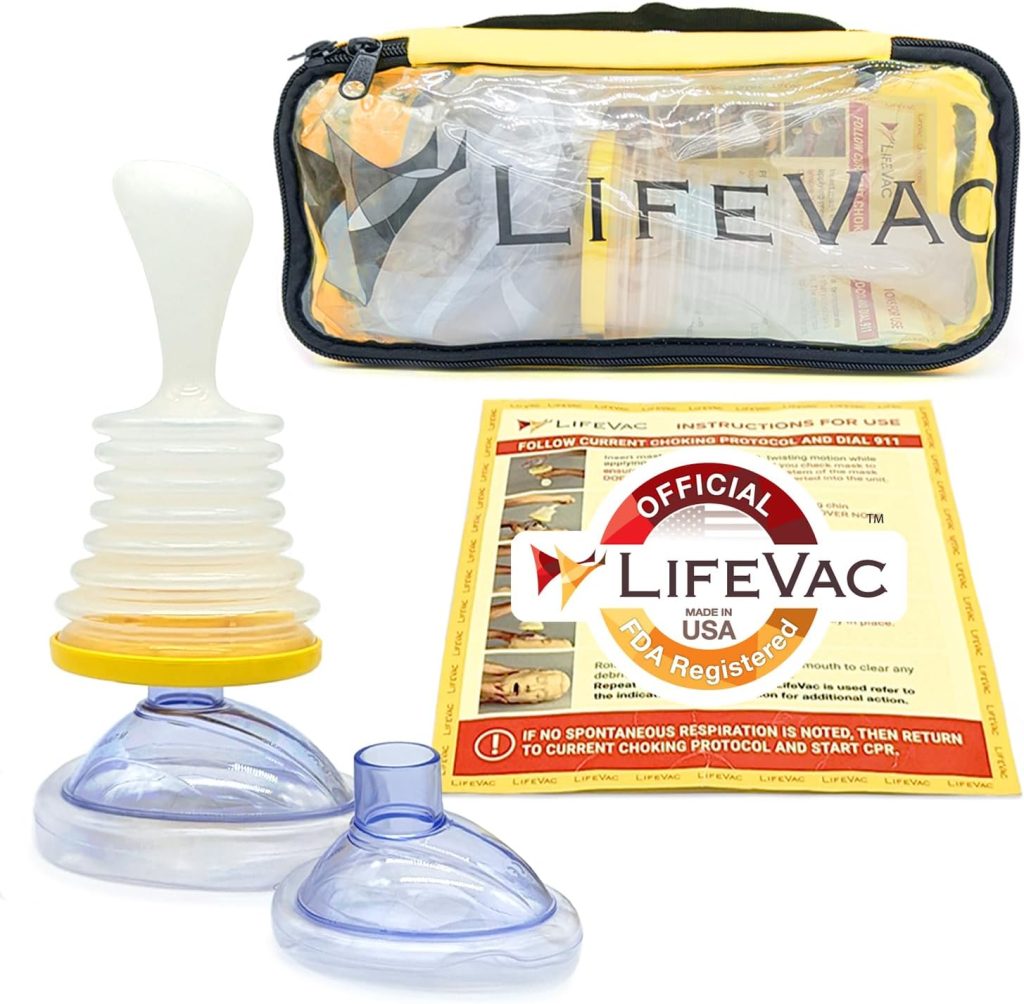
Anti-Choking Device
LifeVac Choking Rescue Device for Kids and Adults
The Urgency of Choking Emergencies
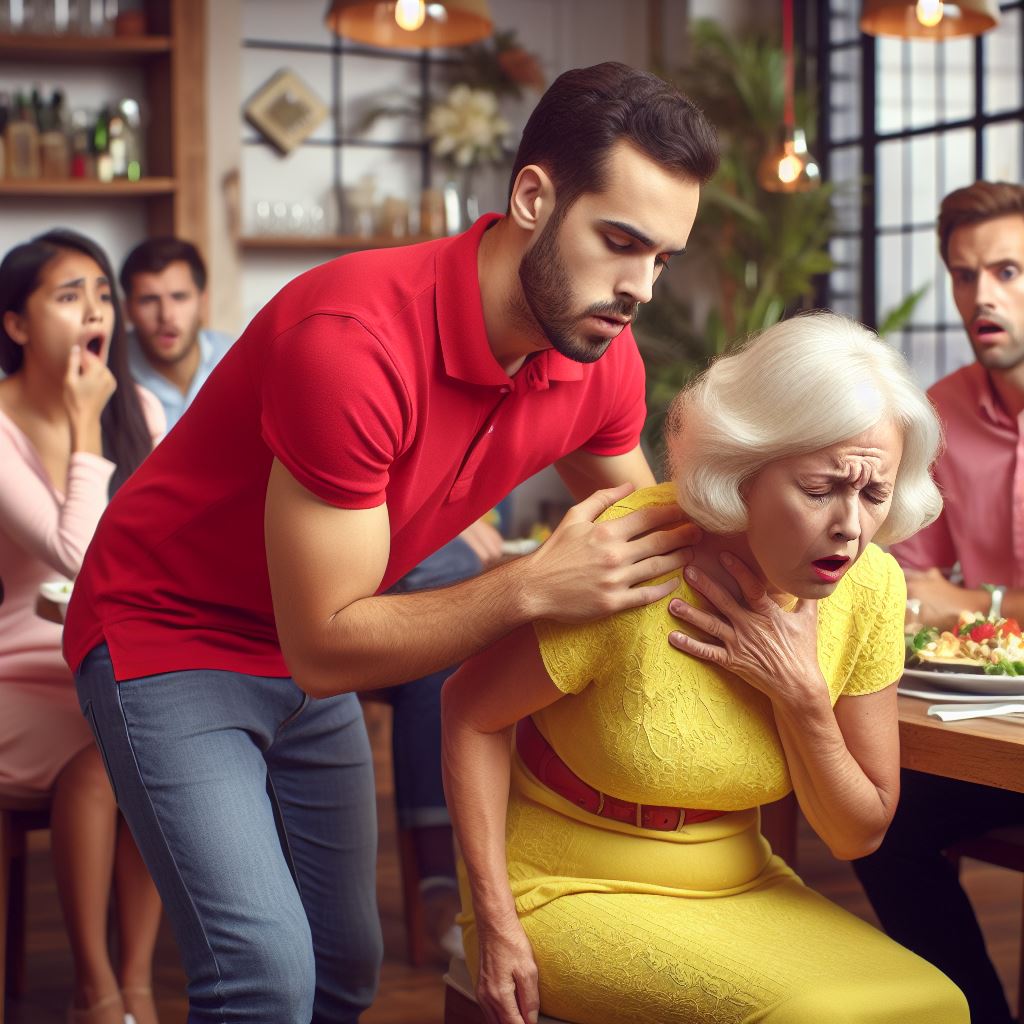
Choking occurs when an object, often food or a foreign body, becomes lodged in the airway, obstructing the flow of air. The urgency lies in the fact that without immediate intervention, oxygen supply to the brain is compromised, leading to potentially fatal consequences. Recognizing the signs of choking and acting promptly can be the key to saving a life.

4 Signs of Choking
- Inability to Speak or Cough: A person who is choking may be unable to speak or cough effectively. They may exhibit panic or distress.
- Gripping the Throat: The universal sign of choking is someone grasping their throat. This gesture indicates a blockage in the airway.
- Difficulty Breathing: Choking individuals may gasp for breath, wheeze, or make high-pitched sounds while struggling to breathe.
- Change in Skin Color: The skin may turn blue or dusky due to a lack of oxygen. This is a critical indicator of a severe choking emergency.
Common Choking Hazards for Different Age Groups
- Children:
- Small Toys and Objects: Small toys, coins, and objects that can fit into a child’s mouth pose a significant choking risk. Always keep small items out of reach.
- Choking on Food: Children may choke on foods like hot dogs, grapes, popcorn, and hard candies. Cut these into small, manageable pieces for young children.
- Adults:
- Choking on Food: Similar to children, adults can choke on certain foods, especially when eating quickly or not chewing thoroughly.
- Alcohol-Related Choking: Alcohol can impair coordination and increase the risk of choking, particularly if combined with eating.
- Seniors:
- Choking on Grapes: Grapes are a common choking hazard for seniors due to their small size and slippery texture. Consider slicing grapes or choosing alternative fruits.
- Denture-Related Choking: Ill-fitting dentures can increase the risk of choking. Regular dental check-ups are crucial for seniors to ensure proper oral health.
Responding to a Choking Emergency
- Act Quickly: Time is of the essence in a choking emergency. Encourage the person to cough forcefully, as this may dislodge the obstruction.
- Perform the Heimlich Maneuver: If the person is unable to cough or is not making any sound, perform the Heimlich maneuver. Stand behind them, place your arms around their waist, make a fist, and perform quick, upward thrusts just above the navel.
- Call for Help: If the person is still choking after attempting the Heimlich maneuver, call emergency services immediately. Continue with abdominal thrusts until help arrives.
- Learn CPR: Basic knowledge of CPR can be invaluable in a choking emergency. If the person becomes unconscious, CPR may be necessary to maintain blood flow and oxygenation.
Worried about a loved one? Panic buttons are great for these situations. If you’re worried about your parents, grandparents, or other at-risk folks – then consider getting them a panic button to make sure they can easily and quickly alert medical professionals and loved ones if something goes wrong.
Preventing Choking Incidents
- Supervise Young Children: Always supervise young children, especially during meals, to prevent them from putting small objects or improperly sized food items in their mouths.
- Encourage Slow Eating: Remind individuals of all ages to eat slowly, chew thoroughly, and savor their meals. Avoid multitasking while eating, especially when consuming challenging foods.
- Food Preparation for Seniors: Caregivers for seniors should pay attention to food preparation, ensuring that it is suitable for their abilities, and consider alternatives or modifications when necessary.
Conclusion
In conclusion, recognizing and reacting to choking emergencies is a vital skill for everyone. Understanding the signs of choking, identifying common hazards for different age groups, and responding promptly with appropriate techniques can save lives.
The Heimlich maneuver is definitely worth learning, and so is basic CPR. Both are easy to learn, and both are capable of helping you save someone’s life.
With that said, we also think anti-choking devices can come in handy, such as the LifeVac one we recommended above.
FAQ
If the person is still able to cough or make sounds, encourage them to keep coughing forcefully. It’s crucial to let them attempt to clear the airway themselves. However, stay vigilant, as the situation may escalate, and immediate action may become necessary.
Yes, the Heimlich maneuver can be performed on yourself. You can use your own hands or lean over a hard surface, such as a table or chair back, to apply abdominal thrusts. However, it’s essential to seek professional medical evaluation afterward to ensure there are no lingering concerns.
Yes, certain foods, such as grapes, can pose a higher risk of choking for seniors due to their small size and slippery texture. Caregivers should consider slicing or cutting these foods into smaller, more manageable pieces to reduce the risk.
To prevent choking incidents in young children, always supervise meals and playtime. Keep small objects, toys, and foods that pose a choking risk out of their reach. Additionally, encourage slow eating habits and teach them to chew thoroughly.
If the person loses consciousness during a choking emergency, immediately call emergency services and begin CPR. Begin chest compressions, and after every 30 compressions, check the mouth for any visible obstruction. If present, remove it and continue CPR until help arrives.